Understanding Embolectomy
Embolectomy is surgery to remove a blood clot (embolus) from one of your blood vessels. The clot may block the flow of blood to your tissues or organs. Removal of an embolus is often an emergency procedure.
How to say it
ehm-boh-LEHK-toh-mee
Why embolectomy is done
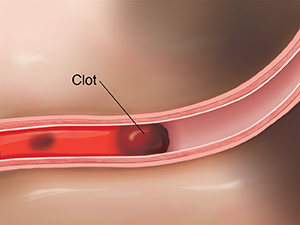
An embolus is a blood clot that has traveled from another part of the body and lodged in a blood vessel. It can block the flow of blood through the vessel. This can cause serious problems, including tissue or organ damage. Removing the clot allows blood to flow freely again.
How embolectomy is done
-
An IV (intravenous) line will be put in a vein in your arm or hand. You may be given medicine to help you relax (sedation) through the IV.
-
You will be given medicine to help prevent pain during the procedure.
-
The healthcare provider will make a cut (incision) through your skin and into the blood vessel with the clot. Or they will make a cut in another blood vessel, so that a tube may be put in to reach the clot. A dye test (angiogram or venogram) may be used to help the provider see the blood vessel and clot on a video screen.
-
The healthcare provider will remove the clot from the blood vessel.
-
The provider may use a thin tube (catheter) to remove any part of the clot that remains. They may put a small mesh tube (stent) in the blood vessel to help hold the vessel open. This is not removed.
-
The blood vessel is closed.
-
The incision is closed and bandaged.
If you've had a stroke, your healthcare provider may advise a procedure called mechanical thrombectomy. A catheter is put into an artery and guided to the clot in the brain. Providers often use the femoral artery for this. The provider puts a clot-removing device through the catheter until it reaches the clot. The provider removes the clot.
Risks of embolectomy
-
Bleeding
-
Infection
-
Damage to the blood vessel or nearby tissues
-
Blood clot fragments dislodging and moving into other parts of the body, including the heart, lungs, or brain
-
Compartment syndrome, which is increased pressure in the muscle that cuts down on the flow of blood
-
Provider may not be able to remove the clot
-
Provider may detect other disease in the blood vessel that will need more surgery to fix
-
Loss of blood supply to the limb, which could result in an amputation