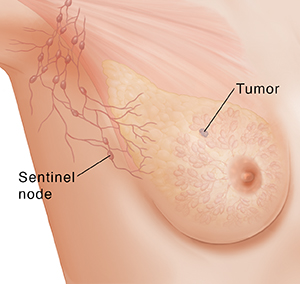
What Is a Sentinel Lymph Node Breast Biopsy?
The lymphatic system is part of the immune system. It's one of the pathways cancer cells can use to travel to other parts of the body (metastasize). It’s made up of lymph nodes and vessels that carry lymph fluid throughout the body. Lymph nodes are small round organs along the vessels that filter the lymph fluid as it flows through. The sentinel node is the first lymph node that cancer cells from the primary tumor drain into. So it’s the first place that cancer is likely to spread. With breast cancer, the sentinel node or nodes are usually in the armpit.
A sentinel lymph node biopsy can be done at the same time as surgery to remove a cancerous tumor and breast tissue (lumpectomy or mastectomy). It might be done when the cancer is in an early stage and there's no sign that it has spread to the lymph nodes. The biopsy may be used to find the lymph node that's most likely to have cancer cells in it.
During the biopsy, one or more of the sentinel lymph nodes are removed. They're sent to the lab for testing. Sometimes the lymph nodes are checked for cancer cells during the surgery.
If there are cancer cells in the sentinel node, more lymph nodes may need to be removed. This might be done right away if the nodes were tested during surgery. It can also be done later as a second surgery. Your surgeon will discuss this choice with you.
If no cancer cells are found in the sentinel node, you won't need to have more lymph nodes removed.
If the sentinel lymph node can't be found during surgery, many or all of the lymph nodes may need to be removed. The actual number will vary from person to person.
A sentinel node biopsy gives your healthcare team valuable information about the cancer. There's also less risk of side effects than when all the lymph nodes in the underarm are removed. (This is called a full axillary lymph node dissection.)
How is the sentinel node found?
There are two ways to find the sentinel node. Your surgeon may use one or both of them:
A blue dye may be injected near the changed breast tissue or into the tumor. It flows into nearby lymph vessels. Then its path into the lymph nodes is tracked. The dye collects in the sentinel node or nodes. Your healthcare provider will talk with you about your allergies to be sure it's safe to use this dye.
A small amount of radioactive tracer solution may be injected near or into the tumor. A gamma detector is then used to find the hotspot where the solution collected. This is the sentinel node.
Understanding the risks
Lymph node surgery involves certain risks. Your surgeon will discuss them with you before surgery. These include:
Infection
Bleeding
Fluid collection (seroma)
Pain or numbness from damage to nearby nerves
Limited arm movement
Long-term swelling of the hand, arm, arm pit, and chest (lymphedema)
Unable to find the sentinel lymph node. This may need another procedure to remove more lymph nodes
Allergic reaction to the blue dye
Talk with your healthcare provider about what you can do to help prevent these problems.
Sentinel lymph node breast biopsy is a complex surgical procedure that needs a lot of skill. Make sure your surgeon has experience doing this type of surgery.