Teens: STI Symptoms (Male)
STI stands for sexually transmitted infection. This means the infection is spread during sexual activity. Viral causes of STIs include hepatitis B, herpes, HIV, and human papillomavirus (HPV). Bacterial causes include chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. STIs can infect the genitals, mouth, and anus. STIs can spread inside the body and harm the reproductive organs. This can may cause a person to be sterile. Sterile means you can’t be a biological parent.
Males may have fewer symptoms of STIs than females. Pay attention to your body. Learn what’s normal for you, and have any symptoms checked out. STIs can only be prevented by not having sex (abstinence). Proper use of condoms (male or female) can help prevent STIs, but not fully.
Male genitals
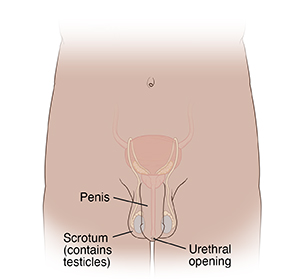
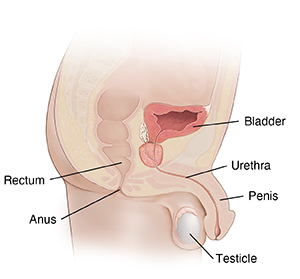
What are the symptoms of STIs?
Common symptoms may include:
-
Discharge (fluid) or a drip from the penis or rectum, which can be yellow, white, green, or clear
-
Burning, pain, or bleeding when you pee or when you move your bowels
-
Sores, warts, or blisters on, in, or around the mouth, genitals, or rectum
-
Lumps or bumps on your genitals
-
Itching on or around your genitals or rectum
-
Pain in your genitals or rectum
What you can do
Keep in mind: You may not have any symptoms. So get checked (screened) if you’re at risk for STIs. Talk with your healthcare provider, school nurse, campus clinic, or local health department for help.
Talk with your partner(s) about STIs and testing. If you have an STI, you will need to encourage your partner(s) to be treated. Otherwise they can pass the infection back to you, or on to others. But it’s important you feel it’s safe to have this talk. If you’re afraid of how your partner may react when you talk about testing, don’t talk face-to-face. Instead, send a text, email, or call. Ask for help before you do this if you feel you’re not safe and your partner might hurt you.