How Seizures Affect the Body
The brain is your body’s control center. It manages everything from movement and balance to emotions and memory. When a seizure happens, some or all brain functions are affected for a short time.
The brain sends signals
The brain sends electrical signals throughout your body. Signals sent from each part of your brain controls a different body function. For example, one part of your brain controls balance. Another part controls speech. A healthcare provider can record your brain signals using a test called an electroencephalogram (EEG).
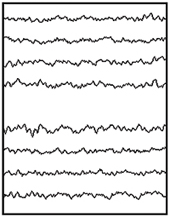
The brain during a seizure
During a seizure, a lot of abnormal electrical signals occur in your brain. They disrupt its normal activity. The way this affects your body depends on 2 main factors:
- Where the seizure happens in your brain. For example, a seizure in a part of your brain that controls movement (the motor cortex) might cause your arm or leg to jerk.
- The spread of the seizure to other parts of the brain. For example, a seizure that affects more of your brain may affect more of your body.
Types of seizures
The types of seizures include:
- Focal seizures. This is when the abnormal electrical activity starts in one part of the brain. These seizures used to be known as partial seizures.
- Generalized seizures. These are seizures that start on both sides of the brain at the same time.
- Unknown onset. This is when it isn't known if the seizure is focal or generalized. It may be hard to know which type until tests such as an EEG are done.
- Focal to bilateral seizure. This is when a seizure starts in one side or part of the brain (focal) and then spreads to both sides.
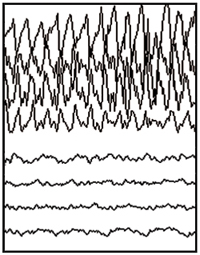
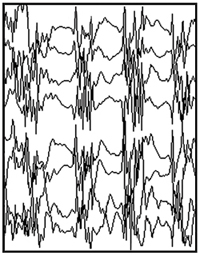
Focal seizures
Focal seizures come in different types. The type depends on any change in awareness. They are:
-
Focal aware. The person having a seizure is awake and aware of their surroundings. They may be unable to talk during the seizure.
-
Focal impaired awareness. People with this type of seizure will have temporary loss of awareness. This can be very brief (few seconds) to much longer. This used to be known as a complex partial seizure.
- Awareness unknown. This is when it can't be determined if the person's awareness is affected or not.
Focal seizures also come in types that describe movements:
- Focal motor seizure. This is when the focal seizure causes abnormal movements. The movements can include twitching, jerking, or stiffening of a body part. Or they can be movements such as licking lips, rubbing hands, walking, or running.
- Focal non-motor seizure. These don't cause movements. But the person may have vision changes, thoughts, or feelings from the seizure.
Generalized seizures
There are 2 kinds of generalized seizures:
- Generalized motor seizure. This is when a seizure happens on both sides of the brain and causes movements such as stiffening or jerking. It's also called a tonic-clonic seizure.
- Generalized non-motor seizure. This is a seizure that affects awareness. It doesn't cause motor symptoms. Some people will have minor movements that repeat, such as blinking or staring. This is also called an absence seizure.
Other effects of seizures on your body
After a generalized motor seizure, you may feel soreness in your muscles when you wake up. Some people bite their tongue during a seizure. Some lose control of their bladder or bowels (incontinence). You may be sweating and have changes in your skin color. If you have seizures in your sleep, you may only know because you feel sore when you wake up. Or you may find you had incontinence while asleep.
Seizures can affect your heart rate, blood pressure, or other vital signs. These changes are often short term (temporary). They get better after the seizure stops. During a seizure, brain cells can be injured, especially with longer seizures. For these reasons, it's important to have good control of seizures.
Seizures that affect your movements or awareness can pose a danger. When a seizure affects awareness, you may be unable to focus on what you're doing. You may lose control of a vehicle or heavy machinery.
Motor seizures (generalized or focal) can lead to injury. With a generalized motor seizure, you can fall and be injured. The motor movements with focal or generalized seizures can cause injury if you're near something dangerous, like a hot stove or a sharp object.
People with seizures that affect awareness or motor function need to take care to prevent injuries. Your ability to drive may be affected. Your driving may be limited. This is based on your provider's advice and local laws. You may need not to swim or shower alone. This is because of the risk of drowning during a seizure. Being up high, such as on a ladder, can lead to serious injury if you have a seizure. Your provider can help you learn what to do to stay safe.