Causes of Lumbar (Low Back) Pain
Low back pain can be caused by problems with any part of the lumbar spine. A disk can herniate (push out) and press on a nerve. Vertebrae can rub against each other or slip out of place. This can irritate facet joints and nerves. It can also lead to stenosis, a narrowing of the spinal canal or foramen.
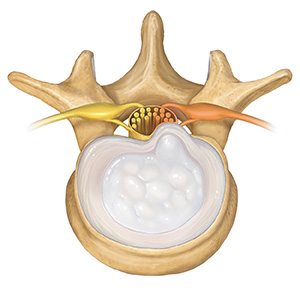
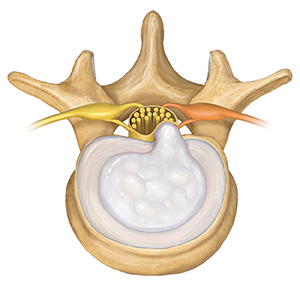
Pressure from a disk
Constant wear and tear on a disk can cause it to weaken and push outward. Part of the disk may then press on nearby nerves. There are two common types of herniated disks:
Contained means the soft nucleus is protruding outward. | Extruded means the firm annulus has torn, letting the soft center squeeze through. |
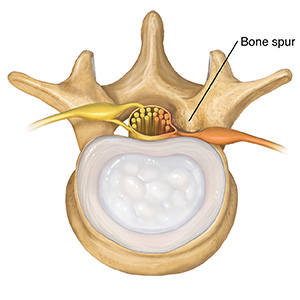
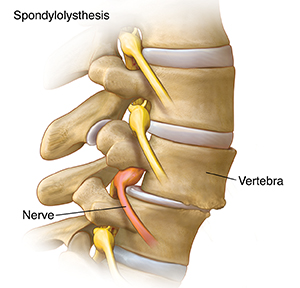
Pressure from bone | An unstable spine |
With age, a disk may thin and wear out. Vertebrae above and below the disk may begin to touch. This can put pressure on nerves. It can also cause bone spurs (growths) to form where the bones rub together. Stenosis results when bone spurs narrow the foramen or spinal canal. This also puts pressure on nerves. | Slipping vertebrae can irritate nerves and joints. They can also worsen stenosis. In some cases, vertebrae become unstable and slip forward. This is called spondylolisthesis. |