Shock Wave Lithotripsy
Passing a kidney stone can be very painful. Shock wave lithotripsy is a procedure that's not surgery. It uses high-energy shock waves to break the kidney stone into smaller pieces. This makes them easier to pass. This treatment is also called extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL). Lithotripsy takes about an hour. You often have it as an outpatient. It's done in a hospital, lithotripsy center, or mobile lithotripsy van. You will likely go home the same day. This treatment is not used for all types of kidney stones. Your healthcare provider will discuss whether this is the right treatment for the type of stone you have.
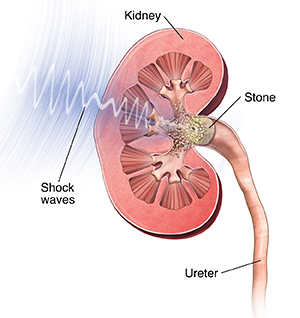
During the procedure
-
You get medicine to prevent pain and help you relax or sleep during lithotripsy. Once this takes effect, the procedure will start.
-
A flexible tube (stent) with holes in it may be placed into your ureter, the tube that connects the kidney and the bladder. This helps keep urine flowing from the kidney.
-
Your healthcare provider then uses X-ray or ultrasound to find exact where the kidney stone is.
-
High-energy shock waves are aimed at the stone and sent at a high speed. If you’re awake, you may feel a tapping as they pass through your body.
After the procedure
-
You’ll be closely watched for about 1 to 3 hours in a recovery area. Antibiotics and pain medicine may be prescribed before you leave.
-
You’ll have a follow-up visit in a few weeks. If you received a stent, it will be removed. Your healthcare provider will also check for pieces of stone. You may need a second lithotripsy or another procedure if large pieces remain.
Possible risks and complications
-
Infection
-
Bleeding in the kidney
-
Bruising of the kidney or skin
-
Blockage (obstruction) of the ureter
-
Failure to break up the stone (other procedures may be needed)
Passing the stone
It can take a day to several weeks for the pieces of stone to leave your body. Drink at least 8 to 12 glasses of water a day. This will help flush your system. During this time:
-
Your urine may be cloudy or slightly bloody. You may even see small pieces of stone.
-
You may have a slight fever and some pain. Take prescribed or over-the-counter pain medicine as instructed by your healthcare provider.
-
You may be asked to strain your urine to collect some stone particles. These will be studied in the lab.
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following:
-
Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your healthcare provider
-
Heavy bleeding
-
Pain that doesn’t go away with medicine
-
Upset stomach and vomiting
-
Problems urinating
- New symptoms or symptoms that get worse